I have a question... If Autos never become dominant then how are certain strains 100% stable Autos? It's confusing for me to think Autos are never dominant but you can stable them to where they produce 100% auto offspring as long as crossed with another stable Auto... 
-
We are moving to Discourse! https://autoflower.discourse.group/
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
- Joined
- Jan 2, 2011
- Messages
- 11,019
- Reputation
- 2,420
- Reaction score
- 7,616
- Points
- 0
- Website
- www.youtube.com
I just answered that the other day in another thread... forget the thread tho... hmmmm
- Joined
- Jan 2, 2011
- Messages
- 11,019
- Reputation
- 2,420
- Reaction score
- 7,616
- Points
- 0
- Website
- www.youtube.com
basically 2 recessive trait parents keep bringing the same pieces to the table... and keep complimenting each other... from my understanding... maybe phree or zy can jump in and elaborate... or maybe correct me... lol
If you're talking about the post a few pages back I saw that... I agree (with my limited knowledge) I just assume some where down the generations the Auto does become dominant... Otherwise, how do we have so many stable Auto strains at this point in time?
The Squid
Spaced-out CephaloMOD
If you're talking about the post a few pages back I saw that... I agree (with my limited knowledge) I just assume some where down the generations the Auto does become dominant... Otherwise, how do we have so many stable Auto strains at this point in time?
I don't believe that most or many of the strains that we grow and are popular are considered stable. That's why there are still at least two phenos if not more of the strain, because they're still a little wild. I could be wrong.
- Joined
- Jan 2, 2011
- Messages
- 11,019
- Reputation
- 2,420
- Reaction score
- 7,616
- Points
- 0
- Website
- www.youtube.com
well refer back to mendel's square:
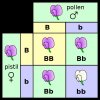

article trunked from:
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/dominant-and-recessive-traits-in-humans.html

I know this article is about humans... but since cannabis is heterozygous... (2 parents male / female) it is virtually the same in relation to recessive and dominant traits... basically the term "dominant" and "recessive" traits are easily misunderstood.What are the Dominant and Recessive Traits?
One of the most important principles that governs life is inheritance of genes. There are over 200 traits that are transmitted from generation to generation in humans. These interesting aspects of human genetics are known as hereditary traits. These hereditary traits include the dominant and recessive traits in humans. Most of the genes are transmitted in the Mendelian pattern and a few are transmitted through the non-Mendelian pattern that includes: co-dominance, sex-linked genes and polygenes.
The physical traits are those that are expressed and what makes every individual an 'individual'. These genes reside on specific segments of the DNA. Each gene is grouped to form a chromosome and each chromosome is found in the nucleus of the cell. There are two copies of each gene present in an individual's body with the exception of eggs and sperms. These two gene copies include one copy of the gene from the mother and one copy from the father. Thus, we see some of our physical traits are similar to our mother and some match our father's traits.
There are two or more variations in most of the genes called alleles. An individual can inherit same pair of alleles or two different pairs of alleles. When there are two different alleles, they are expressed in a different way. The trait that is expressed in case of two different alleles, gives rise to the dominant and recessive traits. When a dominant allele is present, it is always observed that the dominant trait is expressed. The recessive trait is observed only in case there are two recessive alleles present.
It is generally believed that the dominant alleles are the most common traits observed in a population. However, this is not a complete fact. Many times the alleles may be dominant, but the allele for expression of a trait may be recessive. Thus, many times the dominant trait is not expressed in an individual. Let me explain this inheritance pattern in the following examples.

article trunked from:
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/dominant-and-recessive-traits-in-humans.html
- Joined
- Jan 2, 2011
- Messages
- 11,019
- Reputation
- 2,420
- Reaction score
- 7,616
- Points
- 0
- Website
- www.youtube.com
in regards to squids comment... yes... ALL autos are fairly "unstable" in comparison to the older (generationally) photos we have...
autos are at most 15 or 20 generations and considered "stable"... and they are fairly stable... always there will be little nuances hiding in any strain... sometimes they'll come out in sheer numbers... 1 / 100,000 may have that trait... and sometimes that strain meeets another who reinforces that trait... this is part of why selection is SOO important for breeding...
I'm not sure but I'd venture a wild shot at least 50 -100 generations of most "stable" photo strains... see the diff.... how many more selection levels is that? say its 40 even...
40- 15 say = 25 selection points..... thats a lot of optional changes in the shceme of things... all it takes is a selection in a different direction... and you're on a new slightly different strain....
autos are at most 15 or 20 generations and considered "stable"... and they are fairly stable... always there will be little nuances hiding in any strain... sometimes they'll come out in sheer numbers... 1 / 100,000 may have that trait... and sometimes that strain meeets another who reinforces that trait... this is part of why selection is SOO important for breeding...
I'm not sure but I'd venture a wild shot at least 50 -100 generations of most "stable" photo strains... see the diff.... how many more selection levels is that? say its 40 even...
40- 15 say = 25 selection points..... thats a lot of optional changes in the shceme of things... all it takes is a selection in a different direction... and you're on a new slightly different strain....

I guess I wasn't using the correct term... I didn't realize "stable" was a pheno term. I was referring to for example... If I take 20 Purple Jem Autos and grow them... I assume I'll get all 20 autos whether they are males or females... There's still a lot I don't know...
:smokebuds:
:smokebuds:
G
Gandolph420
Guest
Stable isnt a phenotype, stable is just referring to how stable that specific strain is, a lot of strains have many different phenotypes, some strain are more stable meaning that a certain phenotype is dominant over the others so the chance of different phenotype coming through is rare, unstable strains could possibly present a different phenotype in every seed of it you grow.
It can take many, many generations(possibly hundreds of trials) to stabilize a certain phenotype within a plant, it can be brutally pain-staking. This is why i hold any breeder within the highest respect.
It can take many, many generations(possibly hundreds of trials) to stabilize a certain phenotype within a plant, it can be brutally pain-staking. This is why i hold any breeder within the highest respect.
- Joined
- Jan 2, 2011
- Messages
- 11,019
- Reputation
- 2,420
- Reaction score
- 7,616
- Points
- 0
- Website
- www.youtube.com
yes... exactly... more occurence of a particular phenotype indicates a more stable strain... but almost all strains have variable phenotypes... even the old school photos like NL#5
Similar threads
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 115
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 720
- Replies
- 0
- Views
- 288
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 84
